is often called a moment, can informally be thought of as
"rotational force" or "angular force" which causes a change in rotational
motion. This force is defined by linear force multiplied by a radius.
The SI unit for
torque is the newton metre (N m). In U.S.
customary units, it is measured in foot pounds (ft·lbf) (also
known as 'pounds feet'). The symbol for torque is τ, the Greek letter
tau.
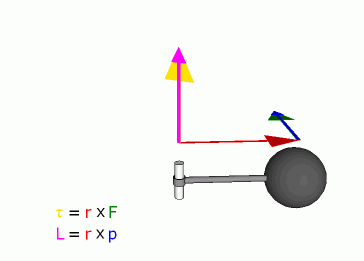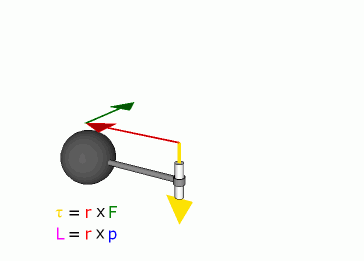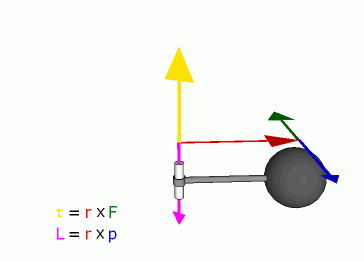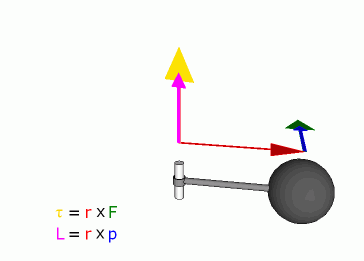
Definition
Angular momentum of a particle about some origin is defined as:
-
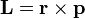
where:
-
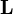 is the angular momentum of the particle,
is the angular momentum of the particle,
-
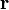 is the position of the particle expressed as a displacement vector from
the origin,
is the position of the particle expressed as a displacement vector from
the origin,
-
 is the linear momentum of the particle, and
is the linear momentum of the particle, and
-
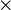 is the vector cross product.
is the vector cross product.
The angular momentum are
newton-meter-seconds;
N·m·s (kgm2s-1).
Because of the cross product, L is a
pseudovector
perpendicular to both the radial vector r and the momentum vector
p.
If a system consists of several particles, the total angular momentum
about an origin can be obtained by adding (or integrating) all the angular
momenta of the constituent particles. Angular momentum can also be
calculated by multiplying the square of the displacement r, the mass
of the particle and the
angular
velocity.
Also see torque
converter.