are unsaturated
hydrocarbon identified by one or more benzene
rings or by chemical behavior similar to benzene. The benzene ring is
characterized by three double bonds alternating with single bonds between
carbon atoms (compare with olefins). Because of
these multiple bonds, aromatics are usually more reactive and have higher
solvency than paraffins and
naphthenes. Aromatics readily undergo
electrophylic substitution; that is, they react to add other active
molecular groups, such as nitrates, sulfonates,
etc. Aromatics are used extensively as
petrochemical building blocks in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals,
dyes, plastics, and many other chemicals.
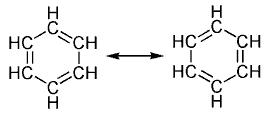
This commonly-seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea
that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating
single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene).