
Newton's Laws of
Gravitation
every single point mass attracts every other point mass by a force
heading along the line combining the two. The force is proportional to the
product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of the
distance between the point masses:
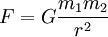
where:
F
is the magnitude of the (repulsive) gravitational force
between the two point masses
G
is the
gravitational constant
m1
is the mass of the first point mass
m2
is the mass of the second point mass
r
is
the distance between the two point masses
F is measured in
newtons (N), m1
and m2 in kilograms (kg), r in metres (m), and the
constant G is approximately equal to 6.67 × 10−11 N m2
kg−2 (newtons times meters squared per kilogram squared).
-


REAL Services
700 Portage Trail
Cuyahoga Falls, OH
44221.3057
voice: 330.630.3700
fax: 330.630.3733
© 1995-2005 REAL Services® U.S.A.
- Analytical Almanac
All Rights Reserved
|