all pumps fall into two major groups: rotodynamic pumps
and positive displacement pumps. Their names describe the method for moving
a fluid. Rotodynamic pumps are based on bladed impellers which rotate within
the fluid to impart a tangential acceleration to the fluid and a consequent
increase in the energy of the fluid. Positive displacement
pumps force liquid to flow in volumetric proportion to decreasing pump
volume. Hydraulic systems are a primary application, wherein the
hydraulic fluid functions as the lubricant. Positive displacement pumps
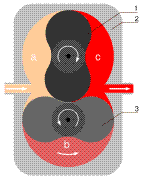
can be divided into reciprocating and rotary. Reciprocating
pumps use pistons, plungers, or diaphragms to increase and decrease volume.
Rotary pumps use a rotating device (gear, screw, or vane) to force liquid
from the pump.
Also see compressor,
pump.