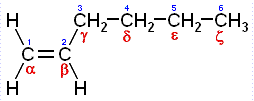polymer derived by polymerization of
relatively simple olefins.
Polyethylene and
polyisoprene are important
polyolefins. A
polymer
produced from a simple
olefin, or
alkene as a
monomer.
For example,
polyethylene is the polyolefin produced by polymerizing the olefin
ethylene.
An equivalent term is polyalkene; this is a more modern term,
although polyolefin is still used in the
petrochemical industry.
Polypropylene is another common polyolefin which is made from
propylene.
A more specific type of olefin is a poly-alpha-olefin (or
poly-α-olefin, sometimes abbreviated as PAO), a polymer made by
polymerizing an alpha-olefin. An alpha-olefin (or
α-olefin) is an alkene where the carbon-carbon
double bond starts at the α-carbon atom, i. e. the double bond is
between the #1 and #2 carbons in the
molecule.
Common alpha-olefins used as co-monomers to give a
polymer
alkyl
branching
groups are similar to
1-hexene
or may be longer.