is the absolute
viscosity of a fluid divided by its density at the same temperature of
measurement. It is the measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow under
gravity, as determined by test method ASTM-D-445.
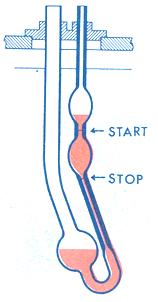
To determine kinematic viscosity, a fixed
volume of the test fluid is allowed to flow through a calibrated capillary
tube (viscometer) that is held at a closely
controlled temperature.
The kinematic viscosity, in centistokes (cSt), is
the product of the measured flow time in seconds and the calibration
constant of the viscometer.
Also see viscosity.
Other methods
include Engler viscosity, Redwood viscosity,
Saybolt Furol and
Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS).