is a molecule having the same molecular formula as
another molecule, but having a different structure and, therefore, different
properties. As the carbon atoms in a molecule increase, the number of
possible combinations, or isomers, increases sharply. For example, octane,
an 8-carbon-atom molecule, has 18 isomers; decane, a 10-carbon-atom
molecule, has 75 isomers.
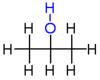
A simple example of isomerism is given by propanol:
it has the formula C3H8O (or C3H7OH)
and two isomers propan-1-ol (n-propyl alcohol; I), propan-2-ol
(isopropyl alcohol; II) an isomer of C3H8O
which has significantly different properties: methoxyethane (III).
|
|
 |
 |
| I |
II |
III |
|
n-propyl alcohol |
isopropyl alcohol |
methoxyethane |
|
C3H7OH |
C3H7OH |
C3H8O |
|
propan-1-ol |
|