is a chemical compound formed by the reaction of an
organic or inorganic acid with an
alcohol or with another organic compound
containing the hydroxyl (-OH) radical. The
reaction involves replacement of the hydrogen of the acid with a
hydrocarbon group. The name of an ester
indicates its derivation; e.g., the ester resulting from the reaction of
ethyl alcohol and acetic acid is called ethyl acetate. Esters have important
uses in the formulation of some petroleum
additives and
synthetic lubricants.
|
|
|
|
|
carboxylic acid
|
R and R' denote any
alkyl or aryl group
|
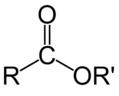 |
|
phosphoric acid ester
|
|
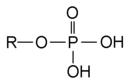 |
Also see dibasic acid ester,
phosphate ester.